Female fetal pig anatomy and simulated dissection worksheet – Embark on an in-depth exploration of female fetal pig anatomy and simulated dissection with this comprehensive worksheet. Designed to provide an immersive learning experience, this guide offers a detailed examination of the pig’s external and internal structures, complemented by a step-by-step simulated dissection process.
Through a blend of descriptive text, clear illustrations, and practical guidance, this worksheet fosters a thorough understanding of the female fetal pig’s anatomy and the techniques involved in its dissection.
Female Fetal Pig Anatomy
The female fetal pig’s external anatomy closely resembles that of a male fetal pig, with a few key differences. The external genitalia of the female pig is less prominent than that of the male. The vulva, the external opening of the reproductive tract, is located on the ventral surface of the body, just posterior to the anus.
The clitoris, a small, erectile organ, is located just anterior to the vulva.The internal anatomy of the female fetal pig is more complex than that of the male. The digestive system is similar to that of the male, with a long, coiled intestine and a single stomach.
The respiratory system is also similar, with a pair of lungs and a trachea. The circulatory system is similar, with a heart and a network of blood vessels.The reproductive system of the female fetal pig is more complex than that of the male.
The ovaries, the organs that produce eggs, are located in the abdominal cavity. The fallopian tubes, the ducts that carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus, are located on either side of the uterus. The uterus, the organ in which the embryo implants and develops, is located in the pelvic cavity.
The cervix, the opening of the uterus, is located at the end of the uterus. The vagina, the muscular tube that connects the uterus to the vulva, is located at the end of the cervix.
Simulated Dissection Worksheet

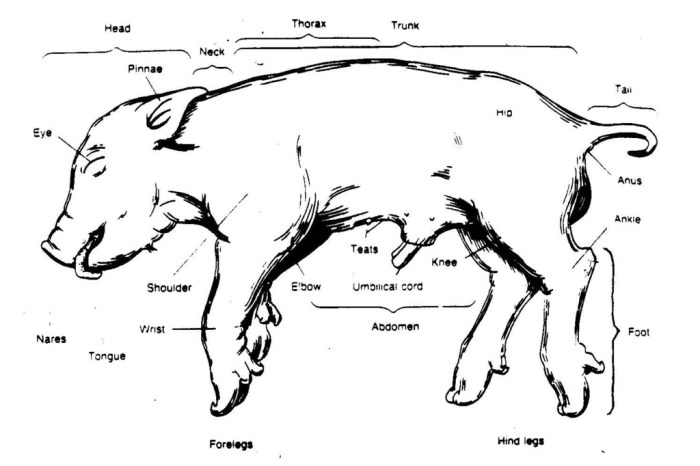
Step 1: External Examination* Examine the external anatomy of the fetal pig.
- Identify the head, neck, trunk, limbs, and tail.
- Identify the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and anus.
- Identify the male or female genitalia.
Step 2: Internal Examination* Make an incision along the ventral midline of the body.
- Open the body cavity and identify the internal organs.
- Identify the heart, lungs, liver, stomach, intestines, and kidneys.
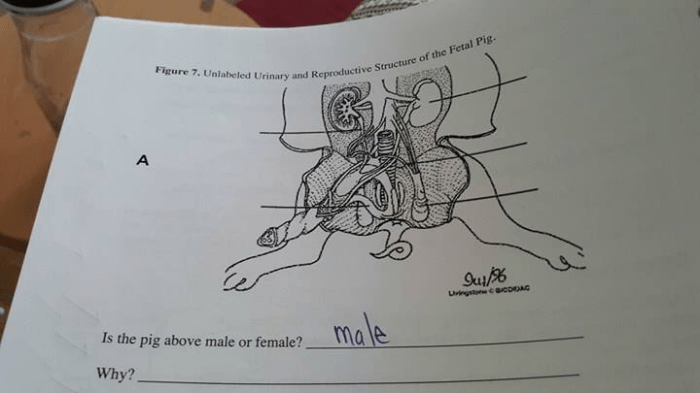
- Identify the male or female reproductive organs.
Step 3: Dissection of the Digestive System* Remove the stomach and intestines.
- Open the stomach and examine the contents.
- Identify the esophagus, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum.
Step 4: Dissection of the Respiratory System* Remove the lungs and trachea.
- Examine the lungs and identify the bronchi and bronchioles.
- Identify the trachea and larynx.
Step 5: Dissection of the Circulatory System* Remove the heart and blood vessels.
- Examine the heart and identify the chambers and valves.
- Identify the aorta, vena cava, and pulmonary artery and vein.
Step 6: Dissection of the Reproductive System* Remove the reproductive organs.
- Examine the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina in the female.
- Examine the testes, epididymides, vas deferens, and penis in the male.
Dissection Techniques: Female Fetal Pig Anatomy And Simulated Dissection Worksheet
The proper dissection of a female fetal pig requires the use of sharp, clean instruments. The dissection should be performed in a well-lit area on a clean surface. The dissector should wear gloves and a lab coat to protect themselves from any potential hazards.The
first step in the dissection is to make an incision along the ventral midline of the body. The incision should be made with a sharp scalpel and should be deep enough to expose the internal organs. The dissector should then carefully open the body cavity and identify the internal organs.The
dissector should then remove the organs one by one and examine them carefully. The organs should be placed in a dissecting tray and labeled for later identification. The dissector should take care not to damage the organs or any of the surrounding tissues.Once
the organs have been removed, the dissector should clean the dissecting tray and the work surface. The dissector should also wash their hands and gloves thoroughly.
Ethical Considerations
The dissection of a female fetal pig is a valuable learning experience for students. However, it is important to remember that the animal is a living creature and should be treated with respect. The dissector should obtain consent from the animal’s owner before performing the dissection.
The dissector should also follow all safety guidelines and dispose of the fetal pig properly after the dissection.
FAQ Insights
What are the key differences between male and female fetal pig anatomy?
The primary difference lies in the reproductive organs. Female fetal pigs possess ovaries, uterine horns, and a vagina, while male fetal pigs have testes, epididymides, and a penis.
What safety precautions should be taken during dissection?
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, a lab coat, and safety glasses. Handle the dissection tools with care and dispose of them properly. Maintain a clean work area and wash your hands thoroughly before and after dissection.
What is the ethical significance of dissecting fetal pigs?
It is essential to approach dissection with respect for the animal and its life. Obtain consent from the animal’s owner and ensure that the fetal pig was obtained from a reputable source. Dispose of the fetal pig remains properly and in accordance with local regulations.