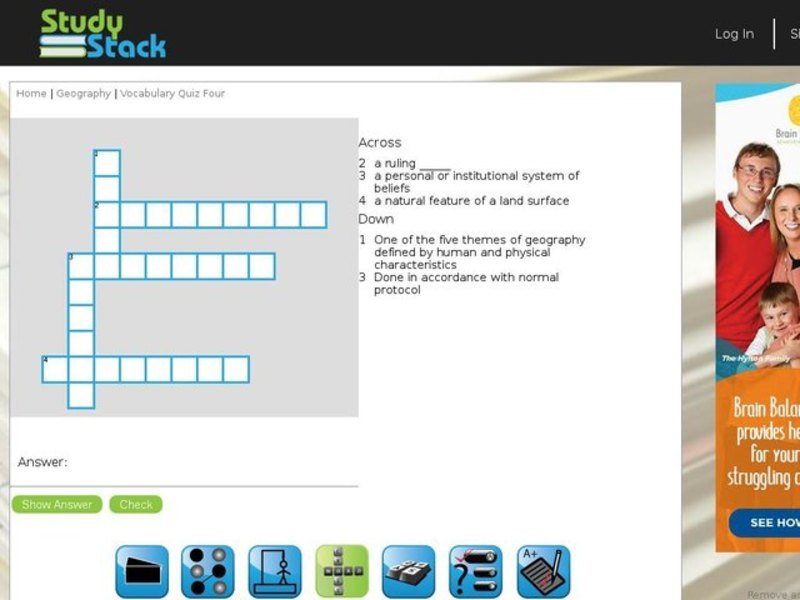
Embark on an intellectual adventure with the Five Themes of Geography Crossword Puzzle, a captivating exploration of the fundamental concepts that shape our understanding of the world around us. This interactive puzzle delves into the intricacies of location, place, human-environment interaction, movement, and region, providing a comprehensive framework for analyzing and appreciating the interconnectedness of our planet.
Prepare to engage your critical thinking skills as you navigate through the clues, unraveling the multifaceted nature of geography. Each theme unveils a unique perspective, shedding light on the spatial distribution of physical and human features, the dynamic relationship between humans and their environment, the flow of people, goods, and ideas, and the significance of regional divisions in shaping global patterns.
Five Themes of Geography
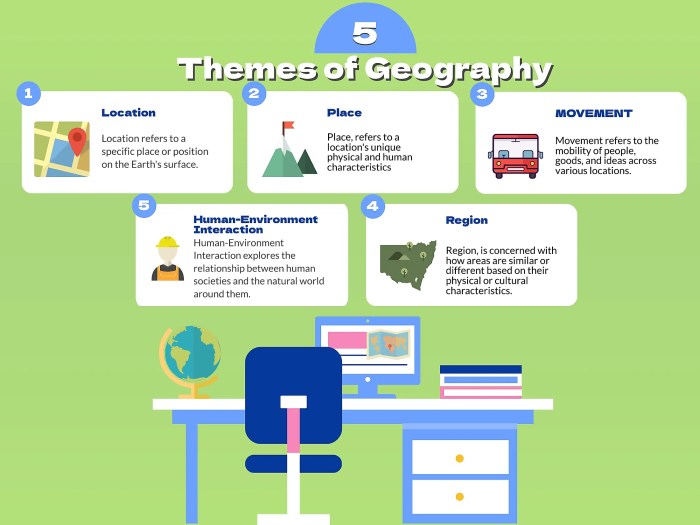
Geography is the study of the Earth’s surface and its human and natural characteristics. The five themes of geography are location, place, human-environment interaction, movement, and region. These themes provide a framework for understanding the world around us and how it has been shaped by both natural and human processes.
Location, Five themes of geography crossword puzzle
Location refers to the position of a place on the Earth’s surface. It can be described in terms of latitude, longitude, and altitude. Location is important because it influences a place’s climate, vegetation, and access to resources. It can also affect a place’s political and economic development.
Place
Place refers to the unique characteristics of a particular location. It includes the physical features of the land, such as mountains, rivers, and forests, as well as the human features, such as buildings, roads, and cities. Place can be described in terms of its physical, cultural, and economic characteristics.
Human-Environment Interaction
Human-environment interaction refers to the ways in which humans interact with their environment. These interactions can be positive or negative. Positive interactions include the use of resources for food, shelter, and clothing. Negative interactions include pollution, deforestation, and climate change.
Movement
Movement refers to the movement of people, goods, and ideas around the world. This movement can be voluntary or involuntary. Voluntary movement includes migration, tourism, and trade. Involuntary movement includes the spread of disease and the forced relocation of people.
Region
Region refers to an area of the Earth’s surface that has similar physical, cultural, or economic characteristics. Regions can be defined by natural boundaries, such as mountains or rivers, or by human boundaries, such as political borders or cultural divides.
Question & Answer Hub: Five Themes Of Geography Crossword Puzzle
What is the significance of location in geography?
Location provides the context for understanding the physical and human characteristics of a place, as it determines its accessibility, resources, and potential for development.
How does place shape our understanding of the world?
Place encompasses the unique characteristics and identity of a particular location, influencing the way people live, interact, and perceive their surroundings.
What are the different types of human-environment interactions?
Human-environment interactions can be classified into three main categories: sustainable, exploitative, and restorative, each with its own implications for environmental health and human well-being.
How does movement contribute to the development of human societies?
Movement facilitates the exchange of ideas, goods, and people, fostering cultural diffusion, economic growth, and the spread of technological advancements.
What is the role of regions in understanding the world around us?
Regions are defined by shared characteristics, such as physical features, cultural practices, or economic activities, and they provide a framework for organizing and analyzing global patterns and processes.