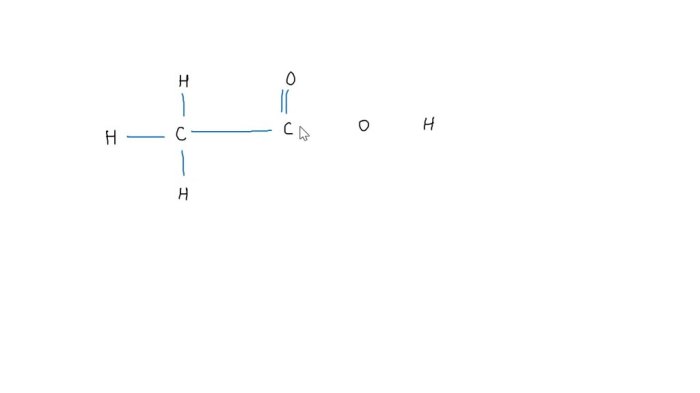
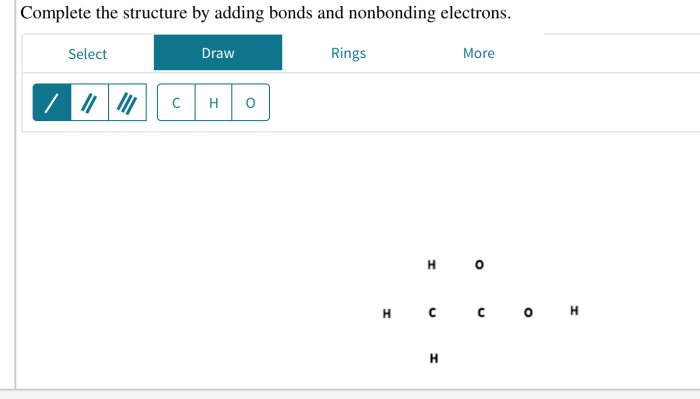
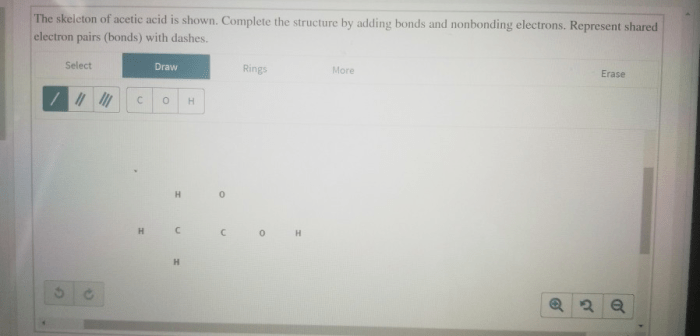
Complete the structure by adding bonds and nonbonding electrons. – Complete the structure by adding bonds and nonbonding electrons, a fundamental concept in chemistry, unveils the intricate world of molecular architecture. By delving into the principles of Lewis structures, resonance, and molecular geometry, this comprehensive guide empowers learners to decipher the language of molecules, unraveling their structures and properties.
Through engaging examples and lucid explanations, this exploration unravels the intricacies of chemical bonding, revealing the interplay between atoms and electrons that shape the molecular realm. Prepare to embark on a journey of discovery, where the building blocks of matter yield their secrets and the enigmatic dance of electrons orchestrates the symphony of molecular existence.
Structural Representation of Molecules
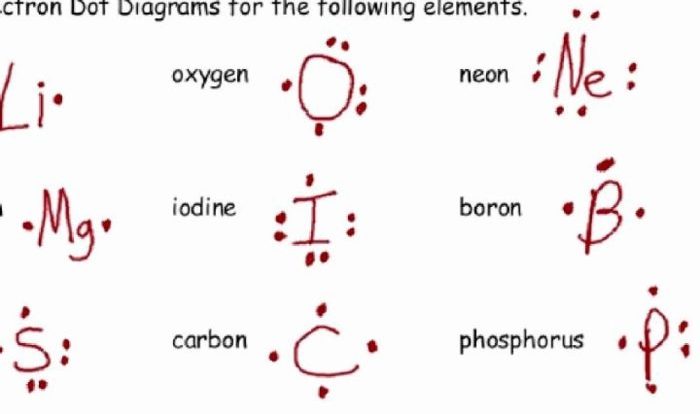
Lewis structures are a convenient way to represent the arrangement of atoms and bonds in molecules. They use symbols for the atoms and lines or dots to represent the bonds between them. Lewis structures can be used to predict the molecular geometry and properties of a molecule.
Adding Bonds and Nonbonding Electrons, Complete the structure by adding bonds and nonbonding electrons.
In a Lewis structure, single bonds are represented by a single line, double bonds by two lines, and triple bonds by three lines. Nonbonding electrons are represented by dots placed next to the atom that they belong to.
Resonance Structures
Some molecules can exist in multiple resonance structures. Resonance structures are different Lewis structures that represent the same molecule. They are used to show the delocalization of electrons in the molecule.
Exceptions to Octet Rule
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain or lose electrons until they have eight valence electrons. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, some atoms can have more than eight valence electrons, while others can have less than eight valence electrons.
Molecular Geometry and VSEPR Theory
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory predicts the geometry of molecules based on the number of bonding and nonbonding electron pairs around the central atom. The VSEPR theory states that electron pairs repel each other and will arrange themselves in a way that minimizes the repulsion.
Hybrid Orbitals and Molecular Bonding
Hybrid orbitals are formed when atomic orbitals combine to form new orbitals that have different shapes and energies. Hybrid orbitals are used to explain the bonding in molecules that have multiple bonds or that have atoms with more than eight valence electrons.
Molecular Orbital Theory
The molecular orbital theory is a quantum mechanical model that describes the electronic structure of molecules. The molecular orbital theory states that electrons in a molecule occupy molecular orbitals, which are formed by the combination of atomic orbitals.
User Queries: Complete The Structure By Adding Bonds And Nonbonding Electrons.
What is the significance of Lewis structures?
Lewis structures provide a simplified representation of molecular structures, depicting the arrangement of atoms and bonds. They are crucial for understanding molecular geometry, bonding, and reactivity.
How does resonance affect molecular structures?
Resonance occurs when multiple Lewis structures can be drawn for a molecule, indicating that the true structure is a hybrid of these resonance structures. This phenomenon influences molecular properties and reactivity.
What is the role of VSEPR theory in predicting molecular geometry?
VSEPR theory predicts the geometry of molecules based on the number of bonding and nonbonding electron pairs around the central atom. It helps visualize the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule.