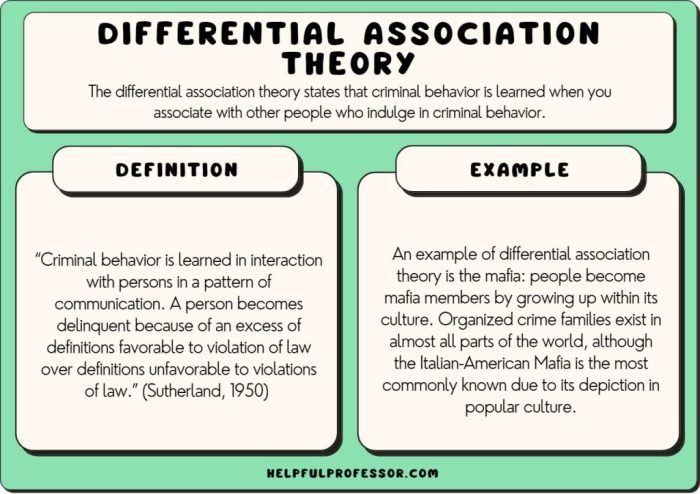
Theories emphasize the role of learning in crime causation, providing a unique lens through which to understand the development and perpetuation of criminal behavior. This perspective underscores the significance of social and cognitive learning processes in shaping individuals’ attitudes, beliefs, and actions, ultimately influencing their propensity to engage in criminal activities.
Social learning theory posits that individuals learn criminal behavior through imitation and reinforcement from their peers and role models. Cognitive learning theory, on the other hand, emphasizes the role of cognitive processes, such as problem-solving and decision-making, in crime causation.
Theories Emphasize the Role of Learning in Crime Causation
Crime causation, the study of factors that contribute to criminal behavior, is a crucial area of criminology. Theories of crime causation seek to explain why individuals engage in criminal activities and identify potential interventions to reduce crime.
Learning plays a significant role in crime causation, as individuals acquire criminal behaviors through various learning processes. This article explores theories that emphasize the role of learning, including social learning theory and cognitive learning theory, and examines empirical evidence supporting their claims.
Social Learning Theory
Social learning theory, rooted in the work of Albert Bandura, proposes that individuals learn criminal behavior through interactions with others. Key concepts include imitation, where individuals observe and imitate the behavior of others, and reinforcement, where individuals are rewarded or punished for their actions.
Social learning theory applies to crime causation by suggesting that individuals who are exposed to criminal peers or role models are more likely to engage in criminal behavior. For example, children who grow up in families or neighborhoods where crime is prevalent may learn to view criminal behavior as acceptable.
Cognitive Learning Theory
Cognitive learning theory emphasizes the role of cognitive processes in crime causation. It suggests that individuals make rational decisions about whether or not to commit crimes based on their perceptions of the costs and benefits involved.
Cognitive learning theory applies to crime causation by proposing that individuals who have a distorted view of the consequences of crime, or who have difficulty solving problems or making decisions, may be more likely to engage in criminal behavior.
Empirical Evidence for Learning Theories
Numerous empirical studies support the role of learning in crime causation.
- Longitudinal studies have tracked individuals over time to examine the impact of learning on criminal behavior, finding that exposure to criminal peers and role models is a significant predictor of future criminal activity.
- Experimental studies have tested the effects of interventions aimed at reducing criminal behavior through learning principles, such as cognitive restructuring and social skills training, demonstrating their effectiveness in reducing recidivism.
Implications for Crime Prevention and Intervention
Understanding the role of learning in crime causation can inform crime prevention strategies by identifying potential targets for intervention.
Evidence-based programs that utilize learning principles to prevent or reduce crime include:
- Mentoring programs that provide positive role models for at-risk youth.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy that helps individuals identify and change distorted thinking patterns.
Limitations and Future Directions, Theories emphasize the role of learning in crime causation
While learning theories provide valuable insights into crime causation, they have limitations.
- They may not fully explain all types of crime, as other factors, such as biological or psychological factors, may also contribute.
- They do not always account for individual differences in learning styles or cognitive abilities.
Future research should explore the role of learning in crime causation further, including longitudinal studies and experimental designs to test the effectiveness of interventions.
Helpful Answers
What is the central tenet of social learning theory in relation to crime causation?
Social learning theory suggests that individuals learn criminal behavior through imitation and reinforcement from their peers and role models.
How does cognitive learning theory explain crime causation?
Cognitive learning theory emphasizes the role of cognitive processes, such as problem-solving and decision-making, in crime causation.
What are some examples of empirical studies that support learning theories in crime causation?
Longitudinal studies have tracked individuals over time to examine the impact of learning on criminal behavior, while experimental studies have tested the effects of interventions aimed at reducing criminal behavior through learning principles.